Search
Malting barley production technology
The organization of the production of malting barley for the needs of our malting plant is an indicator of a successful business model in favor of the satisfaction of our producers. The production contracting conditions for malting barley are known when the contract is concluded. On the basis of the cooperative agreement, we provide our cooperative partners with:
- quality declared seed,
- plant protection products,
- fertilizer and
- agronomic support.
Our team of expert agricultural engineers monitors crops during the growing season and provides producers with expert advice and instructions from sowing to harvesting barley. Our goal is to produce high-quality malting barley and thereby extend partnership cooperation with our cooperators.
Plot selection

Malting barley is not demanding according to the type of soil, which we have established in practice and experience of 15 years, and we have made sure that malting barley grows very well even on soils of a slightly lower quality class. For this type of production, soil with low nitrogen reserves and good water permeability are suitable. Avoid soils that contain more than 2,5% humus, because in rainy years the protein content of the barley grain can be higher than the maximum 11,5% that is required by maltsters. Good pre-seeds are those that leave the field earlier and we have enough time for pre-sowing preparation, for example: sunflower, oilseed rape, soybeans, as well as corn hybrids that quickly release moisture and arrive earlier for harvest. However, due to common diseases between corn and small grains, corn is a less desirable pre-crop for malting barley.
Sowing
We recommend several varieties for sowing, which you can read HERE. These are two-row barleys: winter and springl. The optimal time for sowing winter barley is from the middle to the end of October. Since it is a question of barley, which sprouts very well, the sowing norm is 350.000-400.000 germinated grains/ha, and when we convert it into kilograms, it would be about 180-200 kg/ha (it is necessary to calculate for each batch separately, depending on the mass of 1.000 grains and germination). If it is sown after the optimum period, it is necessary to raise the sowing rate by 10-20%, depending on how late it is.
Spring barley can be sown from the end of October to the end of February. The real recommendation would be to sow as soon as you can enter the field.
Fertilization
Malting barley does not require the same amount of nitrogen mineral fertilizer as some other crops. On the contrary, the amounts of nitrogen fertilizer applied are much reduced in malting barley compared to other crops. To achieve a yield of 1t/ha with the associated vegetative mass, malting barley needs 22kg N/ha.
Basic fertilization: phosphorus and potassium fertilizers should be applied in autumn at the same time as the land is prepared for sowing.
Supplement:
It is recommended that you perform a soil analysis for the content of easily accessible nitrogen one week before the planned supplementation. We recommend supplementation with mineral fertilizers where nitrogen is in an easily accessible form for the plant, AN 34.4% or KAN 27%.
Slow acting nitrogen fertilizers such as 46% UREA have an adverse effect on the protein content of grain, which is a primary parameter in the entire production cycle. Protein intake during harvest must not exceed 11.5%.
General recommendation for nitrogen fertilizer application:
- Application in autumn before sowing: 50 - 60 kg/ha of pure active material N (but depending on soil fertility)
- Top dressing at the end of winter: a minimum of 40 kg N/ha and a maximum of 60 kg N/ha (depending on the amount of readily available nitrogen determined by the N-min method).
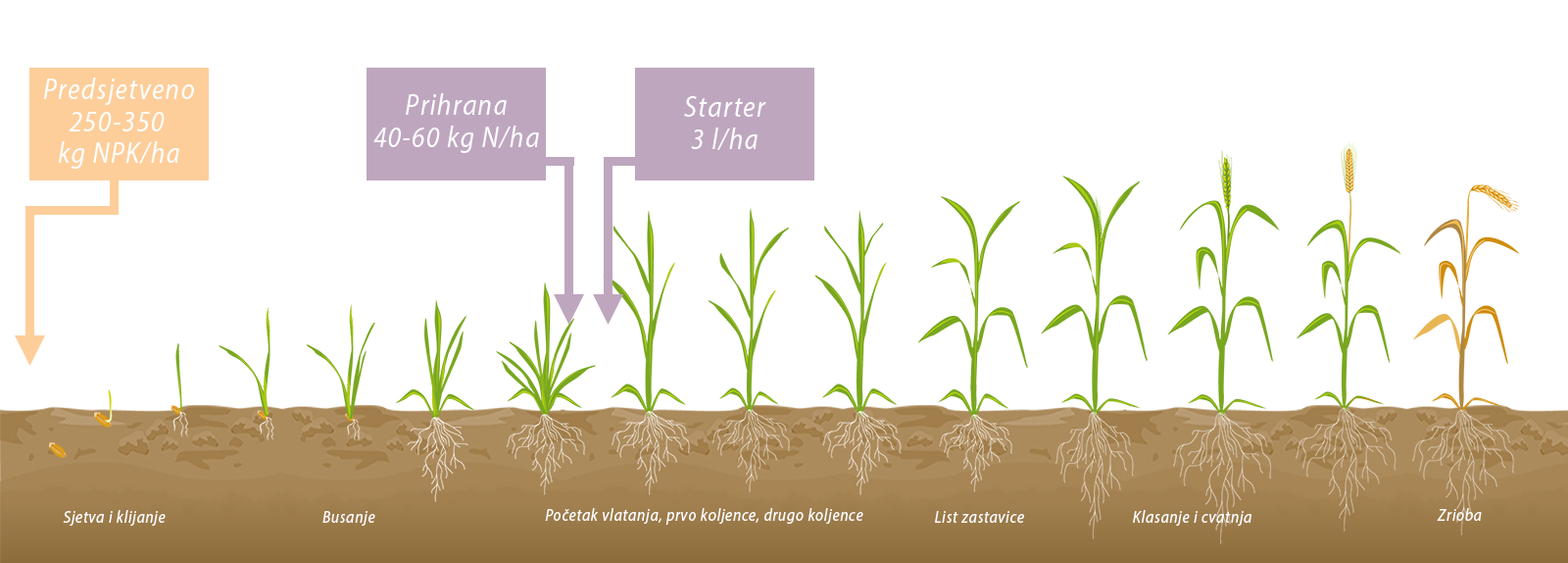
Starter is the brand of Axereal group. A powerful biostimulator that improves the physiological state of the plant, strengthening it against various stressful conditions, especially at the beginning of the growing season when, due to low temperatures, phosphorus is often unavailable to young plants (physiological lack of phosphorus). It helps the absorption of minerals from the soil through the young roots, encourages better nutrition of the plant because nutrients are added in the key phase of growth and development.
The starter consists of a high concentration of easily soluble phosphorus that reaches the leaf surface through foliar application. The starter is compatible with many plant protection products, but before use, perform physio-chemical and biological tests before each use.
Application through the leaf surface: 3 l/ha, from the beginning of budding to the beginning of leafing, second treatment, following the condition of the plant in the 1 cm class phase
Crop care
For our cooperators who have contracted maltng barley, we provide all the necessary raw materials, and ask our experts which plant protection products we recommend.
Our goal is that all our farmers have first-class barley: healthy and high-quality.
For treatments to be successful, external conditions must be respected. At the time of spraying, the daytime temperature must be over 15°C and the following night must not fall below 10°C. After that, for 7 days, the day and night temperature must not fall below 5°C. This is the ideal temperature for fungicide translocation.
T1: is done with the movement of vegetation and the goal is to keep the vegetative mass healthy. Herbicide is also applied there. We recommend the use of insecticides as cicadas have been observed (due to the mild winter).
In order to protect the crop until the beginning of flowering, it is necessary to carry out an intermediate treatment called T2.
T2: a treatment that should also keep the green mass healthy until the fully developed flag leaf phenophase. With barley, it is crucial to keep the spike and 3 leaves below the spike healthy. And T2 enables us to do that.
T3: should be done when the axle starts sticking out of the sleeve. This treatment protects the ear from infection by Fusarium spp and Septoria spp. The importance of this treatment is especially evident when rainfall is expected, because the diseases mentioned are spread by raindrops. If this treatment is missed and an infection occurs, there is no preparation that can stop the aforementioned diseases. That's why our advice is to do preventive treatment and you can calmly expect a good harvest.
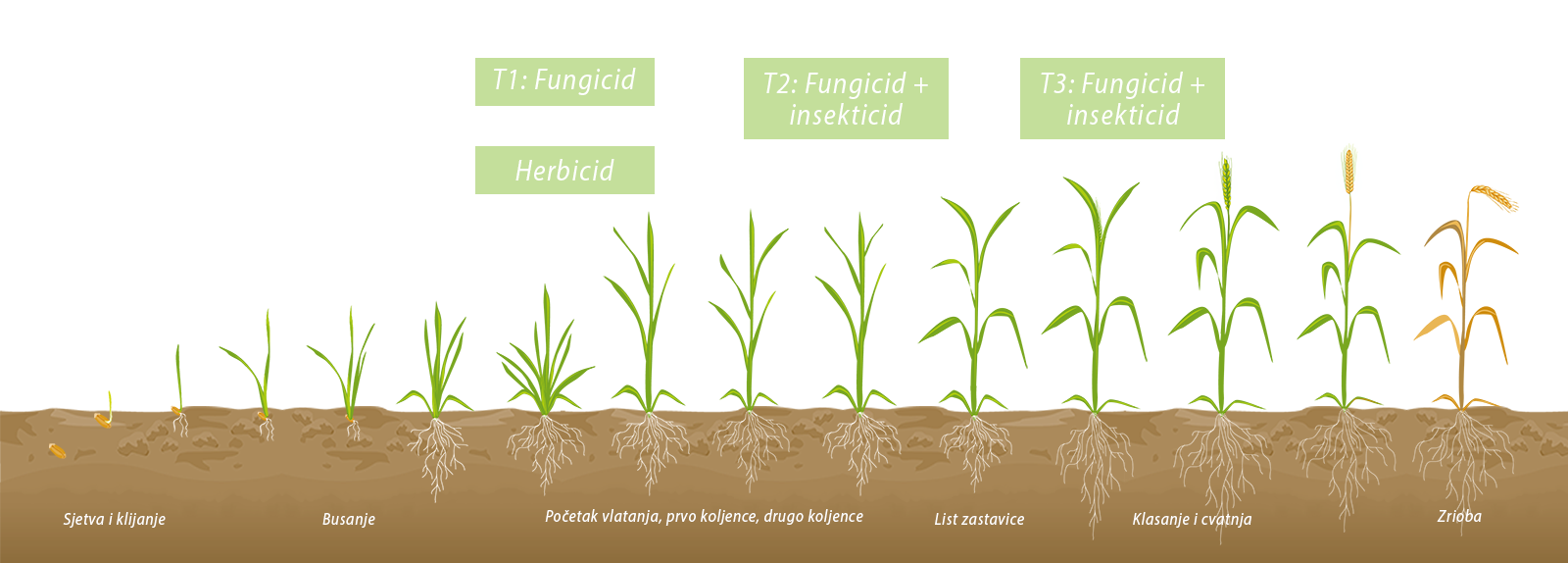
Application of growth regulators is recommended if the crop is too lush and too dense. The most effective are those growth regulators that work to increase the lignin content in the cells, thereby thickening the walls and making the stem stronger and more resistant to lodging. The real effect is achieved if growth regulators are applied in the phenophase of the second knee.
To prevent foaming in the tank when preparing the herbicide mixture, we recommend our product STOP FOAM and read more HERE.
Adjuvant for better effectiveness of herbicides, fungicides and insecticides Hurricane read HERE.
Harvesting, transport and reception at the silo
A few days before the harvest, you need to make an agreement with the commercial representative for the best possible organization of transport and reception in the silo. You should also get the conditions of reception from the commercialist in terms of moisture and the quality of the barley itself. Quality is determined based on sample analysis according to the following parameters that are necessary for brewing barley: protein content, grain calibration, mycotoxin content, grain moisture, etc. This is a standard procedure that the producer is familiar with during the conclusion of the contract.
The reception of goods in the harvest is done at several buying points and with an agreement with the commercialist. When the truck arrives at the silo with barley, a sample is taken from the vehicle and quality analysis is done on the spot by a certified control house, and the agricultural producer can attend the analysis on the spot

